- External Ventricular Drain
- Non-compressible fluid filled catheter with strain gauge and Wheatstone bridge
- Placed in the anterior horn of the lateral ventricle
- Fibreoptic Monitors
- These may be placed in the parenchyma, the ventricles or the epidurally
- Consist of a strain gauge connected to a fibreoptic cable
Considerations for options of ICP monitors
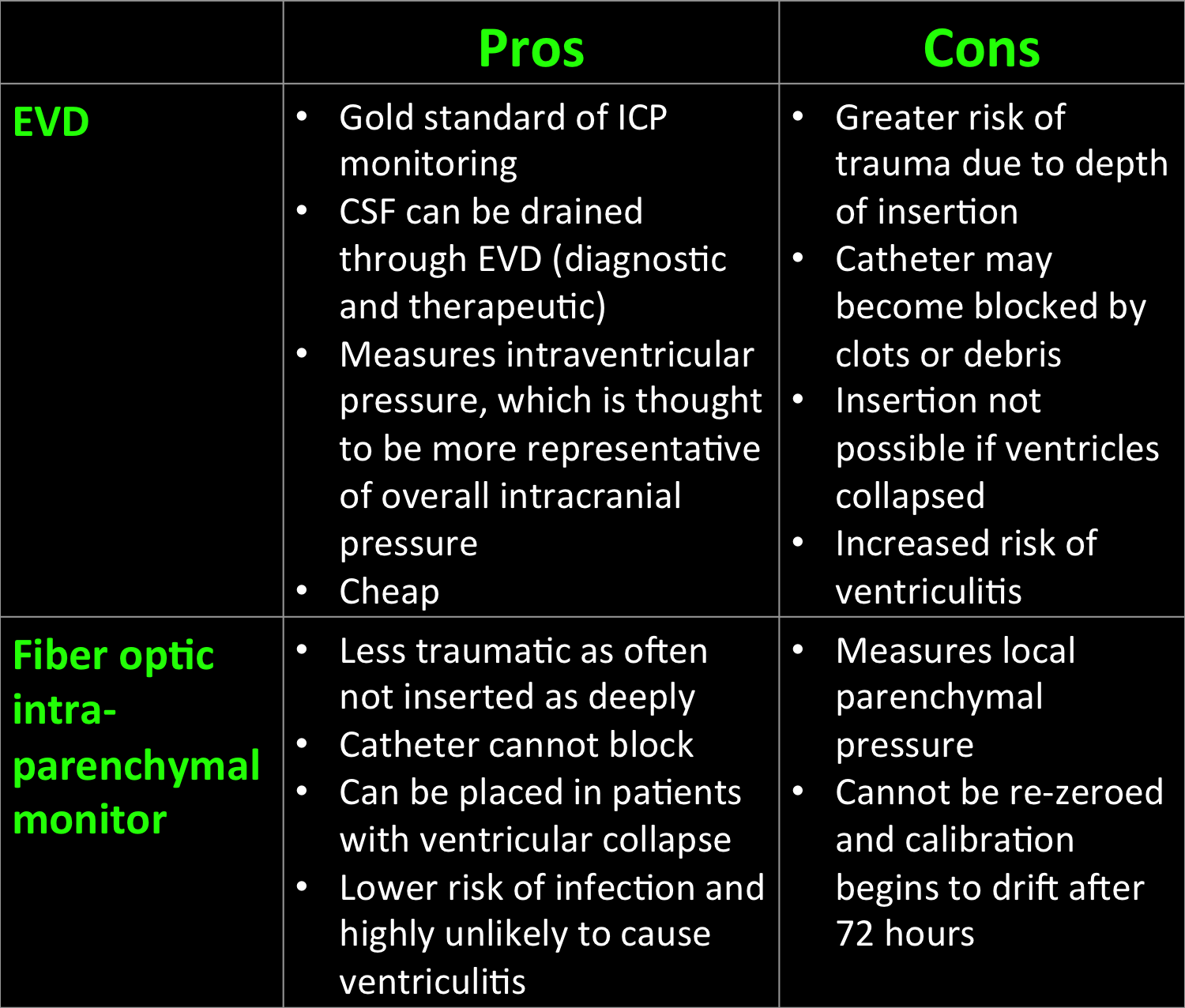
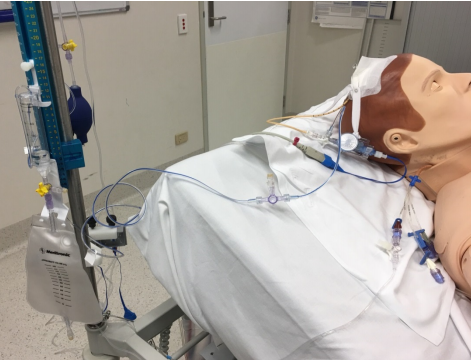
Anatomy of the EVD
- EVD catheter
- Polyurethane cannula inserted surgically into the anterior horn of the lateral ventricle
- Three-way tap
- Connected to the EVD catheter, the drainage catheter and the transducer.
- If the three-way tap is open to the drainage system, the pressure cannot be transduced.
- Pressure transducer
- Strain gauge located on a diaphragm forming part of a Wheatsone bridge
- The pressure transducer is placed at the level of the external auditory meatus
- EVD bacterial filter
- Connected to the transducer
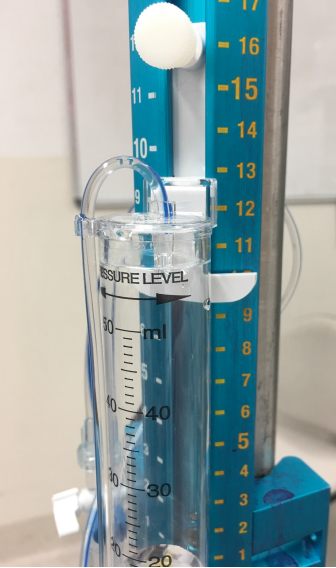
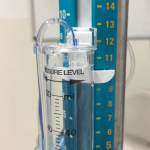
- Drainage catheter and cylinder
- The drainage catheter is connected to the three-way tap and a drainage cylinder
- The drainage cylinder is positioned at a prescribed height above the external auditory meatus
- Ruler
- The ruler allows leveling of the drainage system to the prescribed height above the external auditory meatus
- It allows conversion of centimeters into mmHg e.g. 10cmH2O correlates to 13mmHg
The height of the drainage system above the level of the tragus is prescribed by the neurosurgeons daily. The ruler allows conversion from cmH2O to mmHg. If the drainage system is placed 10cm above the level of the tragus, this correlates to approximately 13mmHg. Therefore CSF will not drain unless the ICP is above 13mmHg. Rapidly dropping the level of the drain may lead to ventricular collapse, extradural haemorrhage or ‘upward’ transtentorial herniation.
- Misplacement of the catheter tip
- Review position on most recent CT brain
- Review the insertion site for signs of catheter migration
- Clots, bubbles, kinks, debris within the catheter
- Check EVD from insertion to drainage system for obstruction
- Review ICP waveform to see if the waveform is dampened
- Check CSF is still draining and whether there is oscillation in the system
- If oscillation is not present, the system may be briefly (less than 5 seconds) lowered to the level of the tragus to check for CSF drainage
- Antimicrobial filter failure
- The antimicrobial filter may become soiled with blood, CSF or saline
- If this is the case it needs to be replaced
- Incorrect zeroing
- The transducer needs to be zeroed to atmospheric pressure at the level of the external auditory meatus
- This may need to be re-zeroed
- Transducer not at the level of the external auditory meatus
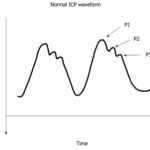
The normal EVD waveform is triphasic, consisting of:
P1- Arterial pulse
P2- Reflection wave which represents cerebral compliance
P3- Dicrotic wave which correlates with the closure of the aortic valve